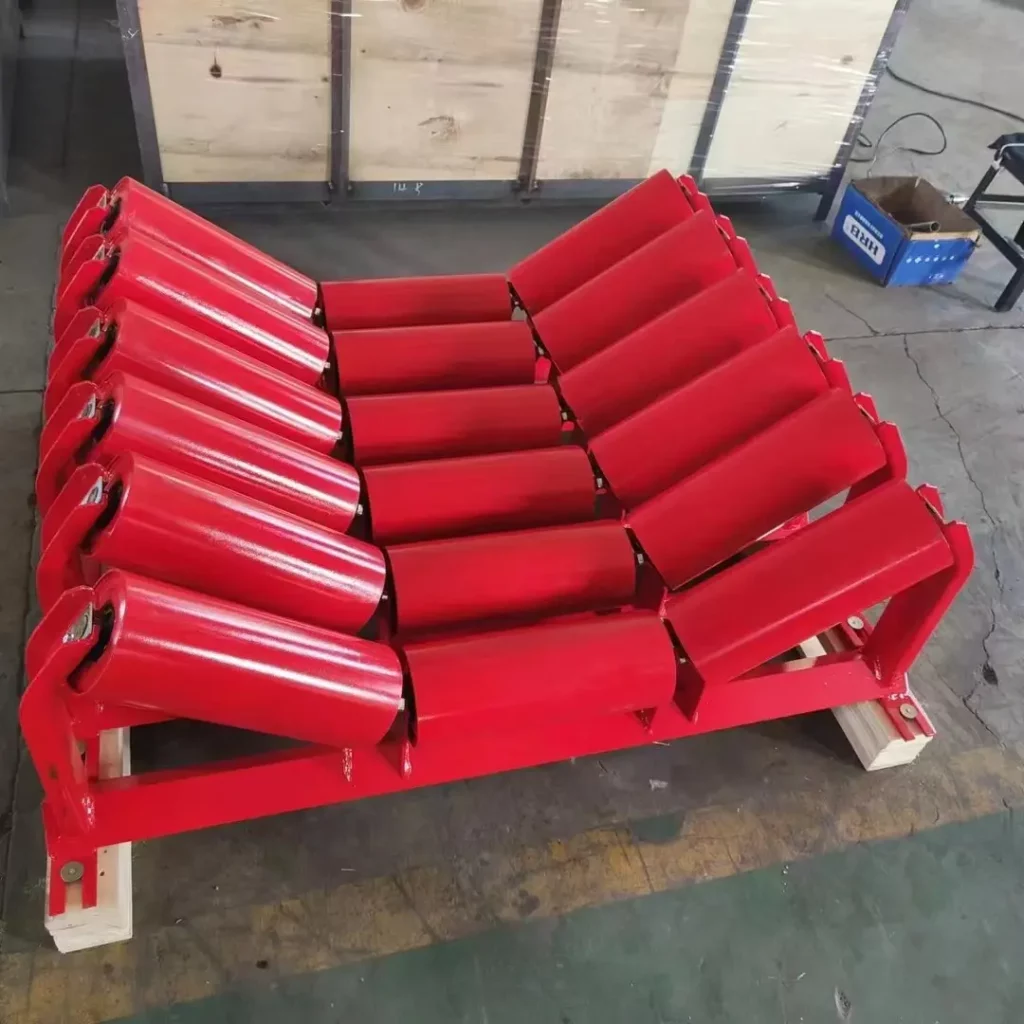
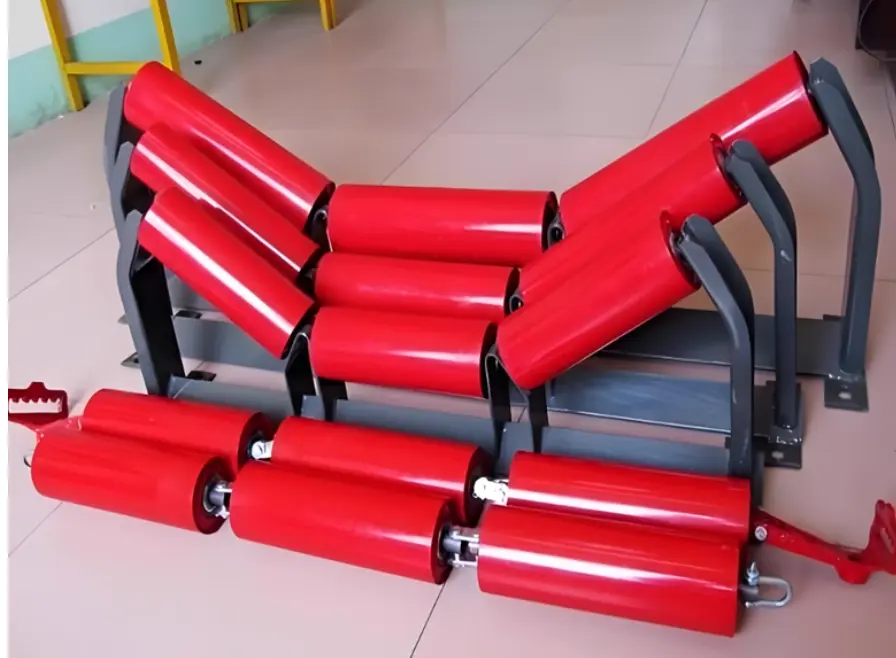




📌 Common Conveyor Idler Roller Models and Sizes
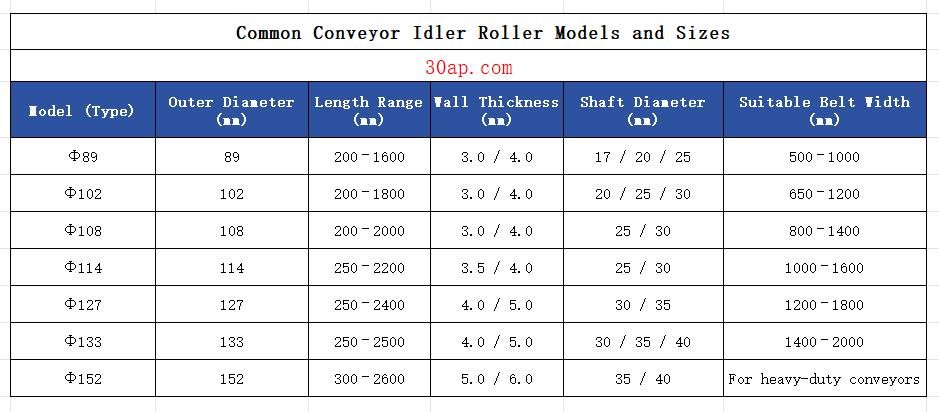
| Model (Type) | Outer Diameter (mm) | Length Range (mm) | Wall Thickness (mm) | Shaft Diameter (mm) | Suitable Belt Width (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Φ89 | 89 | 200–1600 | 3.0 / 4.0 | 17 / 20 / 25 | 500–1000 |
| Φ102 | 102 | 200–1800 | 3.0 / 4.0 | 20 / 25 / 30 | 650–1200 |
| Φ108 | 108 | 200–2000 | 3.0 / 4.0 | 25 / 30 | 800–1400 |
| Φ114 | 114 | 250–2200 | 3.5 / 4.0 | 25 / 30 | 1000–1600 |
| Φ127 | 127 | 250–2400 | 4.0 / 5.0 | 30 / 35 | 1200–1800 |
| Φ133 | 133 | 250–2500 | 4.0 / 5.0 | 30 / 35 / 40 | 1400–2000 |
| Φ152 | 152 | 300–2600 | 5.0 / 6.0 | 35 / 40 | For heavy-duty conveyors |
📎 Notes:
-
Outer Diameter: Refers to the steel pipe diameter of the roller, affecting load capacity.
-
Length: Depends on the belt width; custom sizes available upon request.
-
Wall Thickness: Thicker pipes are more impact-resistant and suitable for harsh conditions.
-
Shaft Diameter: Must match bearings and mounting structure.
-
Types: Includes troughing idlers, flat return rollers, self-aligning idlers, impact rollers, and tapered rollers, etc.
Introduction to Conveyor Idlers
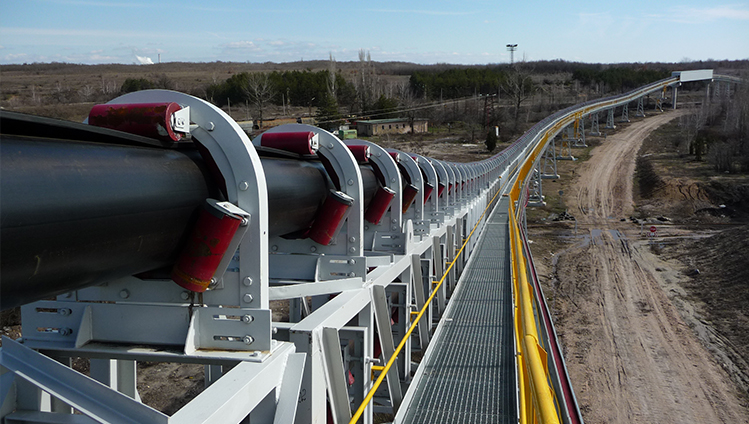
Idlers are essential components of conveyor systems, primarily used to support the conveyor belt and the materials being transported, ensuring smooth and stable operation. Depending on their installation position and function, idlers can be classified into carrying idlers, return idlers, impact idlers, self-aligning idlers, and others.
High-quality idlers are typically made from precision steel tubes, premium bearings, and dust-proof sealing systems. They offer smooth rotation, low noise, and long service life. Idlers are widely used in belt conveyors across industries such as mining, power plants, ports, and cement plants.
Choosing the right type of idler not only improves conveying efficiency but also extends the life of the conveyor belt and reduces maintenance costs.







